Understanding DHT and Its Role in Hair Loss: Causes, Effects, and Treatments
Explore the connection between DHT, hair loss, and male pattern baldness. Learn about effective treatments, side effects, and ways to manage or reduce DHT-related hair loss.
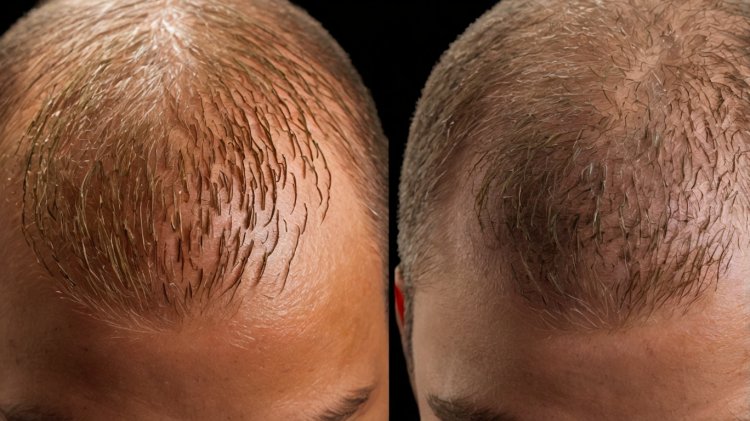
What You Need to Know About DHT and Hair Loss
Hair loss is a common issue that affects both men and women as they age. One of the most significant contributors to this condition is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a hormone derived from testosterone. While DHT plays an essential role in various physiological processes, it can also lead to the gradual shrinking of hair follicles, resulting in thinning hair and baldness.
This guide delves into the role of DHT in hair loss, its effects, and the treatments available to address DHT-related hair thinning.
What is DHT?
DHT, or dihydrotestosterone, is an androgen, a type of sex hormone derived from testosterone. It is produced in small amounts in both men and women and is responsible for many physical characteristics, including body hair growth and voice deepening during puberty.
Approximately 10% of testosterone is converted into DHT by the enzyme 5-alpha reductase (5-AR). While DHT is crucial for certain developmental processes, its influence on hair follicles can lead to hair loss in genetically predisposed individuals.
How DHT Causes Hair Loss
DHT’s connection to hair loss lies in its ability to bind to receptors on hair follicles in the scalp. This binding action causes follicles to shrink, shorten their growth cycle, and become less capable of producing healthy hair. Over time, this leads to thinner hair and, eventually, baldness.
Key Effects of DHT on Hair Follicles:
- Shrinking Hair Follicles: DHT reduces the size of hair follicles, leading to weaker and thinner hair strands.
- Shortened Growth Phase: Hair spends less time growing and enters the resting phase sooner.
- Delayed Regrowth: Follicles take longer to produce new hair after shedding.
Who is Affected by DHT Hair Loss?
Hair loss due to DHT is often hereditary. If you have a family history of male pattern baldness or androgenic alopecia, you are more likely to experience similar hair loss patterns.
- Men: Male pattern baldness typically begins at the temples or crown, progressing over time.
- Women: Hair thinning in women is often more diffuse, with a noticeable reduction in overall hair volume.
Other factors influencing DHT-related hair loss include:
- Variations in the androgen receptor (AR) gene, which may increase follicle sensitivity to DHT.
- Hormonal changes due to aging, medical conditions, or medication use.
Treatments to Reduce DHT and Promote Hair Growth
A variety of treatments aim to reduce DHT levels or block its effects on hair follicles. These include:
1. DHT Blockers
DHT blockers prevent DHT from binding to hair follicle receptors, reducing its follicle-shrinking effects.
- Finasteride (Propecia): An oral medication that inhibits 5-AR activity, reducing DHT production. Studies show it can improve hair count and slow hair loss.
- Pumpkin Seed Oil: A natural DHT blocker that has shown promise in promoting hair regrowth.
2. DHT Inhibitors
Inhibitors target the production of DHT itself, helping to lower its overall levels.
- Herbal Supplements: Pygeum bark and green tea extracts are thought to inhibit DHT production, though more research is needed.
3. Hair Growth Stimulators
These treatments focus on revitalizing hair follicles and encouraging growth.
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): A topical treatment that widens blood vessels to improve scalp blood flow, promoting healthier follicles and hair growth.
- Biotin (Vitamin H): Aids keratin production, essential for strong hair.
Other Treatments to Consider
- Caffeine: Studies suggest caffeine can extend the hair growth phase and improve hair shaft quality.
- Vitamin B Complex: Essential for overall hair health, particularly vitamins B6 and B12, which can help prevent hair thinning.
Side Effects of DHT Treatments
While effective, DHT treatments can cause side effects in some individuals. These include:
- Erectile dysfunction or delayed ejaculation.
- Breast tenderness or gynecomastia (excess fat development in the chest area).
- Skin irritation or rash (with topical treatments like minoxidil).
- Congestive heart failure risk due to fluid retention (rare but possible with minoxidil).
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the best treatment plan and monitor any adverse effects.
Non-DHT Causes of Hair Loss
DHT isn’t the only culprit behind hair loss. Other causes include:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition where the body attacks hair follicles, leading to patchy or total hair loss.
- Thyroid Conditions: Hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism can disrupt hair growth cycles.
- Scalp Infections: Fungal infections like tinea capitis can damage hair follicles, causing temporary hair loss.
- Celiac Disease: Nutritional deficiencies linked to gluten sensitivity may contribute to hair thinning.
- Lichen Planus: An autoimmune disorder that damages skin and hair follicles.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does High DHT Mean High Testosterone?
Not necessarily. While DHT is derived from testosterone, elevated DHT levels don’t always indicate high testosterone. Approximately 10% of testosterone converts to DHT, but genetic factors can influence DHT sensitivity in hair follicles.
Are DHT Blockers Safe?
DHT blockers are generally safe when used under medical supervision. However, they are not a permanent solution and may require ongoing use to maintain results.
Managing Hair Loss: Lifestyle Tips
In addition to medical treatments, adopting healthy habits can improve hair health and slow DHT-related hair loss:
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Include protein, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids for optimal hair health.
- Practice Good Scalp Hygiene: Keep your scalp clean to prevent infections and irritation.
- Stay Hydrated: Proper hydration supports overall health, including your hair.
- Reduce Stress: Stress management techniques like meditation can help minimize hair loss caused by hormonal imbalances.
Conclusion
DHT plays a significant role in male and female pattern hair loss, affecting millions worldwide. Understanding how DHT works and exploring available treatments can empower you to take control of your hair health.
While no single solution can permanently reverse DHT-related hair loss, a combination of medical treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and consistent care can slow its progression and even stimulate regrowth.
Consult a healthcare professional to create a personalized plan that addresses your unique needs and ensures safe and effective hair loss management.
For more insights on hair health and wellness, explore our blog and share this article with others looking to combat hair loss effectively!









